Diabetes Management Guide From Dr. Shima Hadidchi, MD
Dr. Shima Hadidchi, MD, provides a comprehensive approach to diabetes management, blending clinical precision with compassionate, personalized patient care. This guide empowers individuals to take control of their metabolic health through evidence-based strategies and sustainable lifestyle modifications. By focusing on proactive monitoring and tailored treatment plans, Dr. Hadidchi helps patients reduce the risk of complications and improve their daily quality of life. Explore the essential pillars of blood sugar regulation and wellness designed to help you thrive despite a diabetes diagnosis. For more information, contact us or schedule an appointment online. We have convenient locations to serve you in Apple Valley, CA and Victorville, CA.
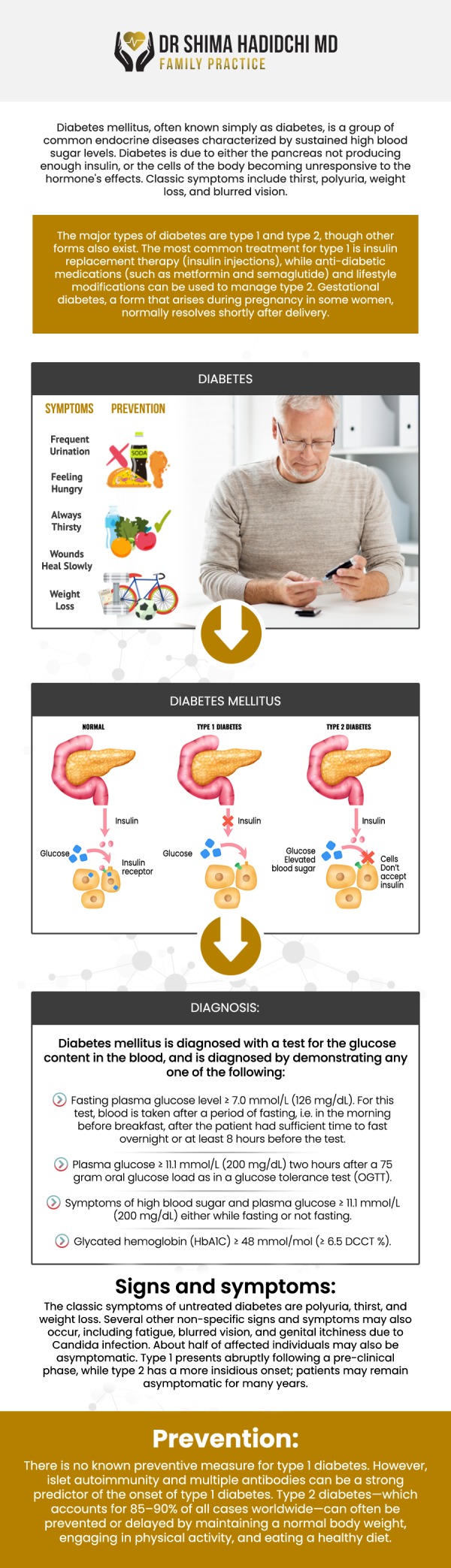
Table of Contents:
Diet & Nutrition
Can weight changes affect my diabetes treatment plan?
What is the “Plate Method” recommended by Dr. Shima?
Which carbohydrates should I avoid?
What role does fiber play in my diet?
Does meal timing matter for blood sugar control?
How does hydration affect blood sugar?
Should I stop drinking alcohol?
Insulin & Medication
Where is the best place to inject insulin?
Why is “site rotation” important?
How should I store my insulin?
What should I do if I’m taking GLP-1 medications like Semaglutide?
Why is timing so important for medication?
What should I do if I miss a dose of my diabetes medication?
How much exercise do I actually need?
When is the best time to exercise?
Does exercise work immediately?
What are the best types of exercise for diabetics?
Can I exercise if my sugar is low?
Is walking after meals helpful for diabetes?
Side Effects & Complications
What are the common side effects of GLP-1 medications?
What are the signs of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)?
What are the “ABC’s” Dr. Shima monitors?
When should I call the doctor immediately?
How does stress affect my diabetes?
Why is foot care important for people with diabetes?
Diabetes management is not a single decision or a one-time treatment—it is an ongoing partnership between the patient and their healthcare provider. Dr. Shima Hadidchi, MD, emphasizes a collaborative approach that integrates medical care with sustainable lifestyle changes. This philosophy recognizes that diabetes affects nearly every system in the body and that long-term success depends on consistency, education, and individualized planning rather than short-term fixes.
Patients living with diabetes often feel overwhelmed by conflicting advice, rigid diet rules, and fear of complications. Dr. Shima’s approach focuses on simplifying care, helping patients understand the “why” behind recommendations, and empowering them to take an active role in their health. By combining evidence-based medicine with practical daily habits, patients can achieve better blood sugar control, reduce complications, and improve their overall quality of life. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of diabetes management, broken into four core pillars: Diet & Nutrition, Insulin & Medication, Exercise & Physical Activity, and Side Effects & Complications.
Nutrition is one of the most powerful tools for managing diabetes, yet it is also one of the most misunderstood. Dr. Shima’s approach to diet is not based on deprivation or extreme restrictions, but on balance, consistency, and understanding how food interacts with blood sugar. Every meal provides information to the body—either supporting glucose stability or contributing to fluctuations that make diabetes harder to manage.
Rather than focusing on perfection, patients are encouraged to build meals that stabilize blood sugar, support energy levels, and fit realistically into daily life. Learning how to structure meals, choose carbohydrates wisely, and maintain hydration creates a strong foundation for effective diabetes management.
Weight changes can significantly influence insulin sensitivity and medication needs. Weight loss often improves blood sugar control and may reduce the need for certain medications, while weight gain can increase insulin resistance and raise glucose levels. Dr. Shima Hadidchi emphasizes monitoring overall trends rather than short-term fluctuations. Treatment plans are adjusted as weight changes occur to ensure medications remain safe, effective, and aligned with the patient’s current metabolic needs.
The Plate Method is a simple, visual approach to meal planning that removes much of the confusion around portion sizes and food choices. Using a standard 9-inch plate, half of the plate is filled with non-starchy vegetables. These include options such as broccoli, cauliflower, spinach, lettuce, tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, zucchini, and green beans. These vegetables are naturally low in carbohydrates and calories but high in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
The remaining half of the plate is divided into two equal sections. One quarter is dedicated to lean protein sources such as fish, poultry, eggs, tofu, beans, or lentils. Protein plays a crucial role in slowing digestion, supporting muscle health, and reducing post-meal blood sugar spikes. The final quarter of the plate is reserved for healthy carbohydrates. These may include whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, or whole-grain pasta; starchy vegetables such as sweet potatoes or corn; or whole fruits.
This method helps patients naturally control portion sizes without counting calories or tracking every gram of carbohydrate. It also promotes consistency, which is especially important for individuals using insulin or glucose-lowering medications. Over time, following the Plate Method teaches patients how to recognize balanced meals, feel satisfied after eating, and avoid extreme blood sugar highs and lows—all while maintaining flexibility and enjoyment around food.
Carbohydrates are not inherently harmful, but certain types can significantly disrupt blood sugar control. Dr. Shima advises limiting refined and highly processed carbohydrates because they are quickly digested and absorbed, leading to rapid spikes in blood glucose. Common examples include white bread, white rice, pastries, sugary cereals, cookies, cakes, crackers, chips, and most packaged snack foods.
These refined carbohydrates are often stripped of fiber and essential nutrients, which means glucose enters the bloodstream rapidly with little to slow absorption. Frequent consumption can worsen insulin resistance over time, making diabetes more difficult to manage even with medication. Sugary beverages such as soda, sweet tea, lemonade, fruit juice, and energy drinks are particularly problematic because they deliver large amounts of sugar without promoting fullness or satiety.
Dr. Shima emphasizes that the goal is not complete elimination but informed moderation. When carbohydrates are chosen carefully—favoring whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and whole fruits—and paired with protein, healthy fats, and fiber, their impact on blood sugar is significantly reduced. Learning to identify which carbohydrates to limit helps patients make confident, informed choices rather than relying on restrictive or confusing diet rules.
Fiber is a critical component of diabetes-friendly nutrition and plays a major role in stabilizing blood sugar levels. Soluble fiber, found in foods such as oats, beans, lentils, apples, berries, and citrus fruits, slows digestion by forming a gel-like substance in the digestive tract. This delays glucose absorption and leads to a more gradual rise in blood sugar after meals.
Insoluble fiber, found in vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds, supports digestive health and helps promote fullness. Together, both types of fiber help regulate appetite, reduce overeating, and support weight management—an important factor in diabetes control. Diets rich in fiber are associated with improved A1C levels, better cholesterol profiles, and reduced cardiovascular risk.
Many people consume far less fiber than recommended, often due to reliance on processed foods. Dr. Shima encourages patients to increase fiber intake gradually to avoid digestive discomfort. Adequate hydration is essential when increasing fiber, as water helps fiber move smoothly through the digestive system. By prioritizing vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and fruits, patients can use fiber as a natural, powerful tool for blood sugar stability and long-term metabolic health.
Yes. Eating meals at consistent times helps prevent large swings in blood sugar levels. Skipping meals or eating very late can lead to spikes or drops, especially for patients taking insulin or glucose-lowering medications. Regular meal timing supports steadier glucose control and better energy throughout the day.
Hydration is often overlooked in diabetes care, yet it plays an important role in blood sugar regulation. When blood glucose levels rise, the kidneys work to remove excess sugar through urine. Adequate water intake supports this process and helps prevent dehydration, which can otherwise concentrate glucose in the bloodstream and worsen hyperglycemia.
Dehydration can also increase fatigue, headaches, and feelings of hunger, which may be mistaken for low blood sugar or lead to unnecessary snacking. Maintaining consistent hydration supports energy levels, digestion, kidney function, and overall metabolic balance.
Dr. Shima encourages patients to prioritize water as their primary beverage. Sugary drinks and even artificially sweetened beverages may interfere with appetite regulation and glucose control. Simple habits—such as carrying a water bottle, drinking water with meals, and increasing intake during physical activity or hot weather—can significantly support daily diabetes management.
Alcohol affects blood sugar in complex and sometimes unpredictable ways. It can initially raise blood sugar, particularly when consumed in sugary mixed drinks, but it can also cause delayed drops in glucose hours later. This delayed hypoglycemia is especially dangerous for patients taking insulin or certain oral medications, as alcohol interferes with the liver’s ability to release stored glucose.
Dr. Shima generally advises avoiding alcohol or limiting it strictly. If alcohol is consumed, it should always be taken with food, never on an empty stomach, and blood sugar should be monitored before and after drinking. Patients should also be aware that symptoms of low blood sugar can mimic alcohol intoxication, making hypoglycemia harder to recognize.
For many individuals, reducing or eliminating alcohol simplifies diabetes management and improves overall health outcomes. Discussing alcohol use openly allows for individualized guidance based on medications, glucose patterns, and personal risk factors.
Medication is a valuable tool in diabetes management, but it is most effective when used in harmony with nutrition, activity, and daily routines. Dr. Shima emphasizes that medications do not replace lifestyle habits; rather, they work best when supported by consistent behaviors and patient understanding.
Insulin should be injected into subcutaneous fatty tissue just beneath the skin. Common injection sites include the abdomen, outer thighs, and the back of the upper arms. The abdomen—at least two inches away from the belly button—is often preferred because it provides the most consistent absorption.
Proper technique is essential. Insulin should be injected at the correct angle using clean needles, avoiding muscle tissue. Understanding injection sites and technique helps ensure predictable insulin action and reduces discomfort.
Repeated injections in the same location can cause lipohypertrophy, a buildup of fatty or hardened tissue under the skin. These areas interfere with insulin absorption, leading to unpredictable blood sugar levels. Rotating injection sites allows tissue to heal and ensures insulin is absorbed evenly.
Dr. Shima encourages patients to rotate within one general area before moving to another, maintaining consistency while preventing tissue damage. Proper site rotation improves insulin effectiveness and long-term glucose control.
Unopened insulin should be stored in the refrigerator to maintain potency. Once opened, most insulin vials or pens can be kept at room temperature for about 28 days, depending on the specific product. Insulin should never be frozen or exposed to excessive heat, such as being left in a hot car.
Patients should routinely check expiration dates and inspect insulin for changes in appearance. Proper storage ensures consistent dosing and reliable blood sugar management.
GLP-1 medications are commonly used for both diabetes and weight management. These medications slow digestion, reduce appetite, and improve insulin response. Dr. Shima emphasizes staying well hydrated, as slowed digestion can increase the risk of nausea or constipation.
Patients are encouraged to eat smaller, balanced meals and monitor for gastrointestinal symptoms, especially during dose escalation. Side effects often improve as the body adjusts. Open communication allows for personalized dosing and supportive strategies to improve tolerance.
The body thrives on routine. Taking diabetes medications at the same time each day helps maintain steady drug levels and prevents gaps in glucose control. Inconsistent timing can increase the risk of high or low blood sugar.
Establishing routines—such as linking medication to meals or daily activities—improves adherence and makes diabetes easier to manage over time.
If a dose is missed, patients should not double up unless specifically instructed. The best approach depends on the medication and timing. Monitoring blood sugar and contacting the care team for guidance helps prevent low or high blood sugar and ensures safe medication use.
Exercise & Physical Activity
Physical activity is one of the most effective non-pharmacologic ways to lower blood sugar. Exercise increases insulin sensitivity and allows muscles to use glucose efficiently, often immediately.
The general recommendation is at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity per week. This can be divided into manageable sessions, such as 30 minutes a day, five days a week. Even short bouts of movement provide meaningful benefits.
Consistency matters more than intensity. Regular activity improves glucose control, cardiovascular health, and overall well-being.
Studies suggest that afternoon or evening exercise may have a greater impact on insulin resistance and post-meal blood sugar control. However, the best time is ultimately the time a patient can maintain consistently.
Monitoring blood sugar before and after exercise helps identify optimal timing.
Yes. During muscle contraction, glucose is taken up by cells for energy without requiring insulin. Even a 10–15 minute walk after meals can significantly reduce blood sugar levels.
A combination of aerobic exercise and strength training is ideal. Aerobic activity improves heart health, while resistance training builds muscle and enhances insulin sensitivity. Flexibility and balance exercises support mobility and injury prevention.
Exercise can further lower blood sugar, so caution is required. Blood glucose should be checked before activity. If levels are low, consuming a fast-acting carbohydrate before starting is recommended. Carrying glucose tablets improves safety.
Yes. A short walk after meals can significantly reduce post-meal blood sugar spikes. Even 10–15 minutes of light activity helps muscles use glucose more efficiently and supports better overall glucose control without intense exercise.
Understanding potential side effects and warning signs allows patients to act early and prevent serious complications.
Gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation are common, especially when starting therapy. These effects usually improve over time. Smaller meals and adequate hydration help reduce discomfort.
Symptoms include shakiness, sweating, dizziness, confusion, headache, and rapid heartbeat. Hypoglycemia often occurs when medication doses exceed the body’s needs or when meals are skipped. Prompt treatment with fast-acting carbohydrates is essential.
• A1C reflects average blood sugar over three months.
• Blood pressure influences cardiovascular risk.
• Cholesterol levels affect the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Together, these markers guide long-term diabetes care.
Immediate medical attention is needed for severe abdominal pain, sudden vision changes, symptoms of pancreatitis, or allergic reactions such as facial or tongue swelling.
Stress triggers hormones like cortisol that raise blood sugar and worsen insulin resistance. Chronic stress can undermine even the best treatment plan. Dr. Shima emphasizes healthy coping strategies, including sleep, movement, relaxation, and mental health support.
Managing stress is a core pillar of effective diabetes care—not an optional one.
Diabetes can reduce circulation and sensation in the feet, increasing the risk of unnoticed injuries and infections. Regular foot checks, proper footwear, and early attention to cuts or sores help prevent serious complications.
Diabetes management is a lifelong journey, but it does not have to feel overwhelming or isolating. With the right guidance, education, and consistent support, patients can move from simply “managing numbers” to truly improving their health and daily well-being. Dr. Shima Hadidchi, MD, believes that sustainable diabetes care is built on trust, understanding, and individualized plans that evolve with each patient’s needs. By addressing nutrition, medication, movement, stress, and prevention together not in isolation patients are better equipped to gain control of their blood sugar, reduce complications, and live full, active lives. This guide is meant to serve as a foundation, but personalized care and ongoing communication with a trusted provider remain the most powerful tools for long-term success in diabetes management. For more information, contact us or schedule an appointment online. We have convenient locations to serve you in Apple Valley, CA and Victorville, CA. We serve patients from Apple Valley CA, Victorville CA, Spring Valley Lake CA, Hesperia CA, Baldy Mesa CA, Mountain View Acres CA, Adelanto CA, and surrounding areas.

Check Out Our 5 Star Reviews


Additional Services You May Need
▸ Telemedicine
▸ Family Practice And Primary Care
▸ Walk-Ins
▸ Weight Loss Management
▸ Zepbound for Weight Loss
▸ Women’s Health
▸ Vaccinations & Immunizations
▸ Diabetes Management
▸ Geriatrics
▸ Pediatrics
▸ Internal Medicine
▸ Acne Treatment
▸ Cryotherapy Treatment
▸ Skin Lesion Removal
▸ Dementia Treatment
▸ Semaglutide GLP-1 Injections

Additional Services You May Need
- Telemedicine
- Family Practice And Primary Care
- Walk-Ins
- Weight Loss Management
- Zepbound for Weight Loss
- Women’s Health
- Vaccinations & Immunizations
- Diabetes Management
- Geriatrics
- Pediatrics
- Internal Medicine
- Acne Treatment
- Cryotherapy Treatment
- Skin Lesion Removal
- Dementia Treatment
- Semaglutide GLP-1 Injections